Sickle cell anemia
Introduction
Inheritance
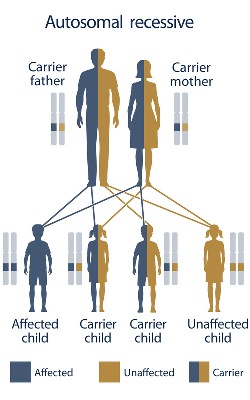 |
| Inheritance of sickle cell anemia |
Sickle cell anemia is inherited from parents in an autosomal recessive manner. The hemoglobin genes that a person inherits from her or his parents determine the forms of hemoglobin that person produces in her or his red blood cells. A child has a 50% probability of having sickle cell illness and a 50% chance of having sickle cell trait if one parent has sickle cell anemia and the other has sickle cell trait. A kid has a 25% probability of developing sickle cell disease when both parents have the trait; 25% do not contain any sickle cell genes, and 50% are heterozygous.
if you want to know about genetics click here
Mutation
 |
| Mutation causing sickle cell anemia |
Symptoms
Following are some symptoms of sickle cell anemia
Ø Anemia.
Sickle cells easily disintegrate and expire. Red blood cells
typically last 120 days or so before needing to be replaced. However, a lack of
red blood cells results from sickle cells, which normally expire in 10 to 20
days (anemia). Fatigue results from the body's inability to obtain enough
oxygen if there are not enough red blood cells.
Ø Hands and foot
swelling.
Sickle-shaped red blood cells obstructing blood flow to the hands and feet are to blame for the edema.
Ø Recurring infections
The spleen may become damaged by sickle cells, making it more susceptible to infections. Antibiotics and immunizations are frequently given to infants and kids with sickle cell anemia to help them avoid potentially fatal illnesses like pneumonia.
Ø Delayed puberty or
growth
The oxygen and nutrients the body needs for growth are delivered
by red blood cells. Lack of healthy red blood cells can prevent teens from
going through puberty and slow down newborns' and children's growth.
Ø Vision issues.
Sickle cells can clog the tiny blood arteries that supply the eyes. This could harm the retina, the area of the eye responsible for processing visual pictures, and cause vision issues.
 |
| Vision problems |
Diagnosis
Following are few tests that can be used to test onset
of sickle cell anemia.
Ø Screening
It has proved very helpful in determining the
diseases.
·
Newborn screening
In some regions it is mandatory to screen newborn baby. This help in early treatment of diseases.
·
Carrier screening
To determine whether parents are carrier for disease or not. If both parents have a defective gene for disease then there are more chances that offspring will have the disease.
Ø Complete blood
count (CBC)
It is done to count number of different types
 |
| CBC |
of blood cells in our blood. This helps in determining the number of RBCs. Low number of RBCs helps to guess sickle cell anemia.
Ø Hemoglobinopathy
(Hb) evaluation
This test is used to measure and distinguish different types of hemoglobin in subject’s body. Following methods are used to do so;
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
Mass spectrometry
Genetic testing through DNA analysis in which DNA
sequencing is done
Ø Blood smear
This is done manually, in which thin layer of blood is examined under microscope and, quantity and quality of RBCs is determined.
Ø Iron studies
This test is performed to assess body’s iron storage and usage. Patients with diseases had received multiple blood transfusions which may lead to iron over loading.
Risk factors
People with following attributes are at greater risk
to fell prey of disease than others;
·
If they have
African ancestry
·
If they have
excessive malaria in there region
· If they work or live somewhere, where mutation causing agents are present more than normal. i. e x-rays, nuclear radiations, or some other agents.

Sickle Cell Anemia Treatment Cost - Sickle cell anemia treatment helps to ease symptoms and prevent complications. Some of the common methods are pain relief, blood transfusions, and hydroxyurea to decrease sickled cells. Bone marrow transplant could cure the disease. Visit: Thalassemia Treatment Cost
ReplyDeleteAplastic Anaemia Treatment Cost
Multiple Myeloma Treatment Cost
Bone Marrow Transplant Cost
Medical Tourism Company